Dbios have exclusive range of Microbiology charts with regular size 50x65cms.
Introduction to Microbiology
Normal Flora
Pathogenicity of Microorganisms
Diagnostic Microbiology
Vaccines And Antibiotics
Bacterial Structure, Growth And Metabolism
Bacterial Genetics
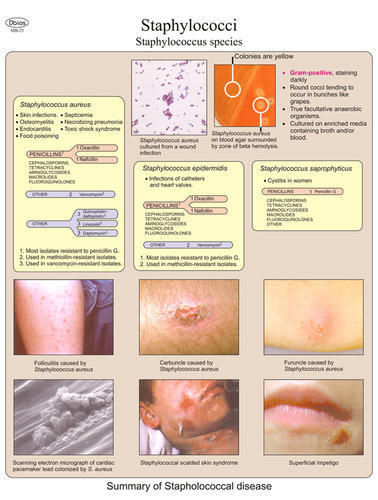
Staphylococci
MB 1 Comparison of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
MB 2 Classification of medically important bacterial families.
MB 3 Classification of medically important virus families.
MB 4 Normal flora in Human Body (Skin, Eye, Mouth and nose,
G. E. Tract, vagina)
MB 5 Bacterial Pathogens Id50 v /s LD50, Adhesion to host cell
membranes, Action of exotoxins, Koch’s postulates.
MB 6 Types of viral pathogenesis, Dissemination of virus to
secondary sites in the body, Mother-to-infant.
MB 7 Laboratory techniques in diagnosis of microbial diseases.
Effect of sensitivity and specificity of a test on the presence
of false-positives and false-negatives. Steps in Gram stain
method.
MB 8 Tests commonly used in identifying bacteria.
MB 9 Immunologic detection of microorganisms.
MB 10 Detection of Microbial DNA or RNA
MB 11 Bacterial Vaccines (DTaP, Childhood immunization)
MB 12 Formulation of Some of the vaccines.
MB 13 VIRAL VACCINES Candidates for hepatitis immunization.
HBsAg = hepatitis B surface antigen.
MB 14 DNAVACCINES produce antigen needed to generate
immunity. MHC = Major histocompatibility complex.
MB 15 Summary of therapeutic applications of selected antiviral
agents.
MB 16 Bacterial cell & Bacterial cell walls.
MB 17 Comparison of gram-positive and gram-negative bacterial
cell.
MB 18 Synthesis of a bacterial cell wall.
MB 19 Bacterial growth.
MB 20 Bacterial genome & Bacterial replication
MB 21 Visual detection of bacteriophage by the plaque method.
MB 22 Gene Transfer – A. Conjugation, B. Transduction, C.
Transformation.
MB 23 Gene Regulation – A. Negative control (repression) B.
Positive control (catabolite activation)
